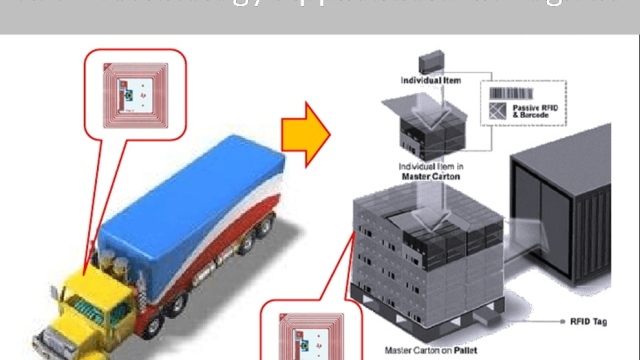
In a world where technology is swiftly advancing, RFID technology has emerged as a key player, revolutionizing the way we track and manage assets. Standing for Radio Frequency Identification, RFID technology utilizes electronic tags to store and transmit data wirelessly through radio waves. From retail to logistics, healthcare to transportation, the applications of RFID are vast and ever-expanding. With its ability to provide real-time information and automate processes, there is no denying that RFID technology is driving us towards a future where efficiency, accuracy, and convenience reign supreme. Discover the incredible potential of RFID technology as we delve into its fascinating capabilities and explore the exciting possibilities it holds for various industries.
1. How RFID Technology Works
In the world of technological innovation, RFID technology has emerged as a game-changer. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) is a wireless technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. The process involves two main components: the RFID reader and the RFID tags.
The RFID reader is responsible for emitting radio waves, which are then received by the RFID tags. These tags, typically small and unobtrusive, contain a microchip and an antenna. When exposed to the radio waves emitted by the reader, the tags power up and transmit their unique identification information, allowing the reader to capture and process the data.
The power of RFID technology lies in its ability to enable fast and accurate automatic identification and data capture. With the ability to read multiple tags simultaneously and from a distance, RFID technology streamlines processes in various industries, including supply chain management, asset tracking, and retail inventory management.
By harnessing the potential of RFID technology, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, improve inventory accuracy, and ultimately make better informed decisions. With its ability to provide real-time data, RFID technology is revolutionizing the way organizations track and manage their assets, resulting in increased productivity and cost savings.
2. Applications of RFID Technology
In recent years, RFID technology has been widely adopted across various industries, revolutionizing the way we track and manage assets. From retail to healthcare, the applications of RFID technology are vast and ever-expanding.
One area where RFID technology has made a significant impact is supply chain management. Retail giants have embraced RFID tags to optimize inventory management, enabling them to track products in real-time throughout the entire supply chain. This not only improves accuracy and efficiency but also allows for better demand forecasting and reduces stockouts. With RFID technology, companies can now have complete visibility of their product movements, ensuring seamless operations and customer satisfaction.
RFID technology has also transformed the healthcare industry. In hospitals, RFID tags attached to medical equipment and supplies help streamline inventory management and improve patient care. By providing real-time tracking information, RFID technology ensures that hospitals have the right equipment at the right time, reducing wait times and enhancing efficiency. Additionally, RFID-enabled patient wristbands improve safety by accurately identifying patients and ensuring proper medication administration.
Another promising application of RFID technology is in the field of agriculture. Farmers can use RFID tags to monitor livestock, track their locations, and gather health data. This allows for better control and management of animal health, preventing the spread of diseases and improving overall productivity. Furthermore, RFID technology can also aid in traceability efforts, allowing consumers to have full transparency regarding the origin and journey of their food products.
With its versatility and efficiency, RFID technology continues to expand its applications beyond these industries. From tracking assets in manufacturing plants to enhancing event management processes, the potential of RFID is limitless. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and impactful uses of RFID technology in the future.
3. Advantages and Challenges of RFID Technology
Advantages of RFID Technology:
-
Efficiency: RFID technology enables fast and automated data collection, eliminating the need for manual scanning. This leads to increased productivity and operational efficiency in various industries such as logistics, retail, and healthcare.
-
Inventory Management: With RFID tags attached to products, businesses can easily track and manage inventory in real-time. This helps in reducing stockouts, minimizing overstocking, and streamlining the supply chain processes.
-
Enhanced Security: RFID technology offers advanced security features, making it difficult for unauthorized users to access sensitive information. Encrypted data and unique identifiers on RFID tags help protect against counterfeiting, theft, and tampering.
Challenges of RFID Technology:
-
Cost: The deployment of RFID technology can be expensive, especially for small businesses. The costs involved include purchasing RFID tags, readers, and software, as well as integrating the system with existing infrastructure. However, as technology advances and adoption increases, the overall cost is expected to decrease.

-
Privacy Concerns: RFID tags can be read remotely, raising concerns about privacy and data security. There is a potential risk of unauthorized surveillance or tracking individuals without their consent. Appropriate measures must be in place to ensure privacy protection and secure data handling.
-
Integration and Compatibility: Integrating RFID technology into existing systems can be complex and time-consuming. Compatibility issues may arise when trying to connect RFID readers with different software or databases. Successful implementation requires thorough planning and coordination with IT teams and stakeholders.
In conclusion, despite the challenges, RFID technology offers significant advantages in terms of efficiency, inventory management, and enhanced security. As the technology continues to evolve and become more accessible, addressing the challenges mentioned will contribute to its widespread adoption and realization of its full potential.